Table of Contents
Psychedelic assisted Therapy
How PAT can change lives according science
Recent research has shown that psychedelic-assisted therapy can speed up progress in treating mental health conditions. Psychedelic drugs, such as psilocybin (found in magic mushrooms, MDMA (also known as Ecstasy), and LSD have shown promising results in treating depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
The accelerated progress of psychedelic-assisted therapy can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the effects of the psychedelic drug create a state of mind that is more conducive to therapy. With reduced defenses and increased introspection, individuals are more willing and able to delve into their emotions and experiences. Secondly, the session itself is often more intense and impactful than traditional therapy sessions, leading to deeper emotional processing.
Psychedelic-assisted therapy will revolutionize mental health treatment. With its ability to rapidly reduce symptoms of mental health disorders, it offers a promising solution to those who have struggled with traditional therapies.
MDMA Therapy
The power of MDMA sessions
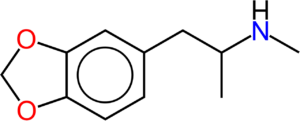
MDMA is a psychoactive substance that can significantly reduce symptoms of PTSD, anxiety disorder, and trauma. According to recent studies, MDMA has a unique ability to downregulate the amygdala, which leads to a decrease in the fear response and emotional reactivity associated with past traumatic experiences.
The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure in the brain that is primarily responsible for processing emotions like fear and anxiety. When a person experiences a traumatic event, the amygdala becomes hypersensitive and can easily trigger the fear response even when there is no real threat. Over time, this can lead to the development of PTSD, anxiety disorder, and other mental health conditions.
MDMA works by releasing a cascade of neurotransmitters, which include serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline, within the brain. Serotonin is particularly important since it regulates mood, anxiety, and social behavior. The release of this neurotransmitter stimulates the frontal cortex and reduces the activity of the amygdala, leading to a decrease in the fear response and emotional reactivity.
During the MDMA therapy session, patients are given a precise dose of MDMA, and then they are allowed to talk about their traumatic experiences without feeling overwhelmed by the fear and anxiety associated with it. The therapy often involves immersive and interactive experiences such as talking with a trusted therapist, listening to music, or engaging in other sensory activities to help patients feel less anxious or fearful.
Psilocybin Therapy
The magic of psilocybin mushrooms and truffles
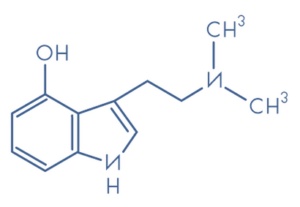
Psilocybin is a powerful psychoactive substance found in certain types of mushrooms. It has been used for centuries by indigenous cultures for ceremonial and healing practices. Recently, scientific research has begun to explore its potential therapeutic benefits for mental health disorders.
Psilocybin that has been converterted to psilocin by the body stimulates the serotonin receptors in the brain, leading to altered states of consciousness and profound psychological experiences. These experiences can lead to increased or decreased self-awareness, enhanced empathy and social connectedness, and a sense of interconnectedness with nature and the universe.
Research has shown promising results for using psilocybin to treat depression and social anxiety. A recent study at Johns Hopkins University found that a single dose of psilocybin, administered under controlled conditions, led to significant improvements in depressive symptoms for up to six months. Another study at New York University found that psilocybin helped to reduce social anxiety in individuals with advanced-stage cancer.
LSD Therapy
The benefits of LSD as an aid during PAT
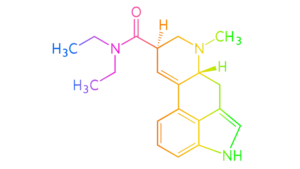
LSD is a potent psychedelic substance and a powerful hallucinogenic drug. Despite being deemed illegal for recreational use in many countries, scientists have continued to investigate its potential therapeutic effects. In recent years, there have been a few controlled studies exploring the use of LSD as an adjunct to psychotherapy for various psychiatric conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
One study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology found that a single dose of LSD (between 100-200 micrograms) led to significant and lasting improvements in anxiety and mood symptoms in patients with life-threatening illness-related anxiety. The study also found that the experience was generally well-tolerated, and the participants reported a sense of increased optimism and openness that persisted for several weeks after the therapy session.
Another study published in the Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease examined the effects of LSD therapy in patients with anxiety-related to life-threatening illness. The study found that the treatment resulted in a significant reduction in anxiety, improved quality of life, and decreased symptoms of depression.
Furthermore, a review published in The Lancet Psychiatry examined six randomized controlled trials of LSD-assisted psychotherapy in patients with depression and anxiety and found that the treatment led to significant short-term improvements in anxiety and depression symptoms compared to a placebo.
The proposed mechanism of action of LSD in psychological therapy is believed to be related to the drug’s ability to alter perception and generate a sense of introspection and emotional insight. The altered state of consciousness brought on by LSD may facilitate the process of psychotherapy by allowing patients to access deeply buried emotions and memories and view their problems in a different light.

